Earth Day: The Best Of Green IT

This week's Earth Day celebration sheds new light on technology's role in creating a sustainable world -- all the more important as rough economic times force businesses to seriously re-assess their spending on power in the data center and beyond. Meanwhile, in the U.S., federal stimulus funds are being directed towards Green IT as well, as projects to create a smart power grid and digitalize health-care records kick off.
In the following pages, ChannelWeb.com takes a look at some of the most environmentally friendly -- and bottom-line boosting -- technologies on offer from top vendors of IT products and services.
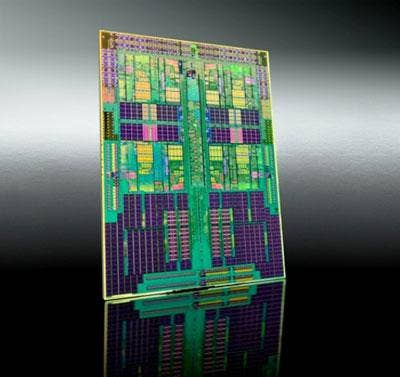
Advanced Micro Devices' newly released Opteron 2373 EE and 2377 EE processors offer the lowest power draw in AMD's lineup of quad-core, 45nm server chips. Formerly code-named Shanghai, this processor family now includes 3.1GHz, 105-watt performers for two-socket and multisocket servers, as well as the two EE parts for two-socket platforms, which draw just 40W while still managing frequencies of 2.1GHz and 2.3GHz.
How It Works: AMD-P is a set of features included in all Opteron processors to directly address power management. Highlights include the chip maker's CoolCore technology, which turns off unused parts of the processor, and Smart Fetch, which allows idle cores to enter a "halt" state, in which data from the L1 and L2 cache are flushed to the shared L3 cache, causing them to draw even less power during processing idle times. Finally, AMD Power Cap technology is a platform-level feature that allows IT data center managers to set a fixed limit on a server's processor power consumption.

Intel calls its Xeon 5500 series of server processors the "greatest Intel Xeon performance leap in history." The new chips, formerly code-named Nehalem, have set more than 30 new benchmark records for two-socket server performance, in areas as diverse as database crunching and virtualization. But as powerful as these microprocessors are, Intel's green value proposition is that replacing eight older, energy-draining single-core servers with the new quad-cores will yield the same overall performance.
How It Works: Intel's Turbo Boost, a power management feature present in the top range of Xeon 5500 chips, acts as a circuit breaker to dynamically shut off individual processor cores that aren't in use. That will likely show up as savings on the energy bill, but the power savings also can be sent over to the cores that are processing workloads to give them some extra oomph. Nehalem also brings back Intel's hyper-threading technology and a number of other improvements to the previous Core generation of Xeon chips that boost power, energy efficiency or both.
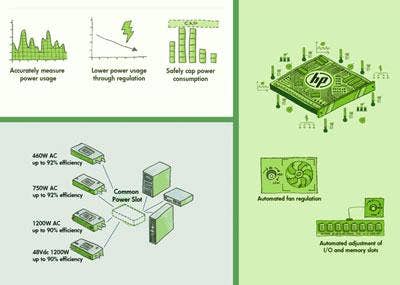
Hewlett-Packard has introduced a slew of green-oriented, cost-saving tools to its latest lineup of HP ProLiant G6 servers based on Intel's quad-core Xeon 5500 series of server processors. These include, clockwise from the top left, Dynamic Power Capping, the "Sea of Sensors" and Common Power Slots. The upshot: HP promises a stunning three-month return-on-investment for businesses replacing older single-core ProLiants with the new systems.
How It Works: Dynamic Power Capping is baked into the ProLiant G6 hardware to stop the power consumption from spiking suddenly, responding to and redistributing new workloads in under a second. HP's "Sea of Sensors" technology leverages a collection of 32 smart sensors located inside every G6 server, providing fine-grained environmental monitoring throughout the system to prevent over-cooling and adjusting fan speeds to avoid wasting power. Finally, HP has devised interchangeable power supplies across all 11 new G6 servers, enabling the stocking of spares and resulting in better than 92 percent power efficiency for the majority of server workloads.

Many businesses are turning to virtualized desktop products like Hewlett-Packard's HP t5630 Thin Client, left, and the HP Compaq t5730 Thin Client, to cut costs and achieve environmentally friendly goals. Thin clients provide up to 80 percent power savings over traditional PCs with similar capabilities, according to the company, and experience just one-quarter the failure rate.
How It Works: Unlike traditional "thick" client PCs, HP's thin client systems have no hard drives, fans or other moving parts, resulting in significantly lower power draws, but also in longer lifespans for the products themselves. Another way thin clients and virtualized desktops save businesses money in green-oriented fashion is through their manageability. It's generally possible to monitor and service such units almost entirely from a centralized, remote location -- essentially eliminating less efficient, more costly and ultimately energy-draining desk-side visits and truck rolls to service traditional PCs.
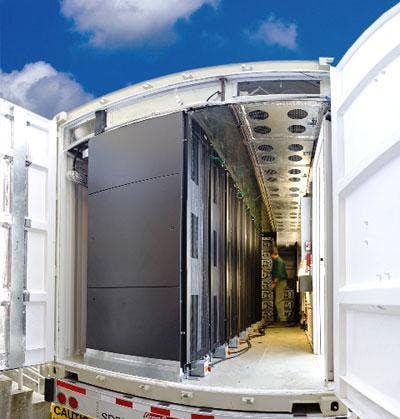

Modular, containerized data centers like Hewlett-Packard's Performance Optimized Data Center (POD), seen here, are in their early stages but generating excitement as easily deployable, power-efficient alternatives to building out physical plants to accommodate IT infrastructure. Other companies with similar containerized data centers include Sun Microsystems, Rackable, IBM, Verari Systems and other smaller system integrators.
How It Works: The beauty of data center containers like HP's POD are that they arrive at a site prebuilt in a modular shipping container -- the same boxes that revolutionized the mass transport of goods around the world. Environmental savings revolve around avoiding the costs and impact of building out physical infrastructure on a site to accommodate a new data center or data center expansion.
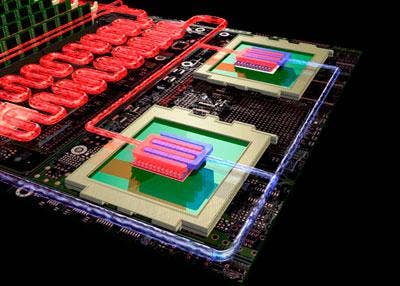
The Power 575 is IBM's premier hydro-cluster supercomputer, featuring not just an innovative water-cooling system but also 448 processor cores per rack that provide more than five times the performance of its predecessor. Advanced water cooling and POWER6 efficiencies make it three times more energy-efficient per rack.
How It Works: The cooling system uses water-chilled copper plates located above each microprocessor to remove heat from the electronics. Requiring 80 percent fewer air-conditioning units, the water-cooled Power 575 can reduce typical energy consumption used to cool the data center by 40 percent. IBM scientists estimate that water can be up to 4,000-times more effective in cooling computer systems than air.

The BladeCenter HS22 from IBM is a no-compromise, two-socket blade with breakneck speed, offering outstanding performance, flexible configuration options and simple management in an efficient server designed to run a broad range of workloads. Among other features, the revamped HS22 features three times as much memory as its predecessor, which allows the HS22 to process twice as many transactions per minute.
How It Works: In conjunction with IBM's Systems Director 6.1, which includes Active Energy Manager 4.1, the BladeCenter HS22 is a data center platform that can be managed both as a physical and virtual resource for consolidation ratios as high as 11-to-1 when switching out older rack and blade servers. That can translate to energy savings of more than 93 percent measured against the power draw of the older systems. Also included is IBM's BluePath Cooling design, which creates "virtual wind tunnels" through the entire blade to keep all of its vital parts cool even under strenuous conditions.

Dell's PowerEdge servers utilize the company's latest power and cooling technologies, (inset), to help drive energy efficiency and better performance in the data center. Other key "green" focus areas for Dell in the data center include virtualization and full server utilization.
How It Works: Dell's combination of efficient modular fan design and Low Flow fan technology controls fan speeds based on the thermal requirements of its servers, while right-sized power supplies and Power Management software also shave wattage from the power draw. Dell also provides customers with infrastructure consulting services, specializing in virtualization, consolidation and migration as paths to a greener data center.

Sun Microsystems' newly released open network Sun Fire servers based on Intel's Xeon 5500 series processors include the Sun Fire X2270, (pictured), and the Sun Fire X4170. The X2270 offers 3x the performance at 66 percent the energy consumption of current generation systems and is especially compact -- delivering savings of up to 50 percent in data center real estate. The four-socket X4170 is a 4U system in a compact 1U form factor, translating to savings of up to 75 percent in rack space, while consuming 60 percent less energy at half the price of similar servers.
How It Works: Sun's integration of solid state drives in the new Sun Fire lineup results in 38 percent less power consumption than with mechanical drive-only systems. Meanwhile, the company's collaboration with Intel in readying its Solaris operating system for the new Xeon 5500 platform has resulted in energy-saving tools like Power Aware Dispatcher, which automatically monitors and optimizes the system to maximize performance while minimizing power consumption -- for example, by utilizing Intel's new Deep C-States to dramatically reduce power consumed by idle cores.

The SPARC Enterprise T5440 server sold by both Fujitsu and Sun utilizes the multithreaded UltraSPARC T2 Plus processor to deliver the massive throughput of up to 256 simultaneous compute threads and 512 GB of memory in just four rack-units of space, while consuming 95W and featuring a number of unique power management tools. Virtualization and consolidation tools are also featured.
How It Works: Automated tools baked into the SPARC Enterprise T5440 include power management features that park idle threads, while the server's Intelligent Fan Control adjusts rotational fan speed according to changes in temperature, thereby reducing power consumption. The T5440 design also maximizes power savings by dividing the chassis and fans into cooling zones that allow a response only from those fans needed to compensate for changes in temperature.
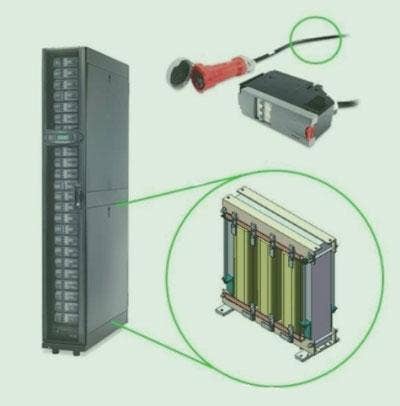
Power and cooling infrastructure is a key driver of the energy efficiency of a data center. While traditional power distribution units (PDUs) take 480 volt power from an uninterrupted power supply (UPS) and transform that voltage down to 208V/120V using an isolation transformer, APC has a greener method of getting the same job done with its auto transformer-based 415V Modular PDU.
How It Works: Auto transformers experience as much as 10 times less energy loss than isolation transformers. Not only does this reduce electrical consumption in the PDU, but it also reduces heat-generated and subsequent cooling costs. Auto transformers are also less than half the size of isolation transformers for the same power rating. That means less copper used in manufacturing and less weight to ship. Finally, delivering power at 415V/240V to servers allows for less current and thus smaller power cables, also reducing the copper used in the data center.

Eaton's BladeUPS is a highly energy-efficient uninterruptable power supply for the data center, providing a normal operating efficiency in the 97 percent range, with Competitive Model normal operating efficiency at 91.5 percent. The payoff -- one 60kW solution can save a customer more than $6,000 per year in energy costs as well as reduce requirements for air-conditioning systems.
How It Works: With Eaton's BladeUPS, data center managers have the ability to flex the power system to meet changing business requirements, while the system itself achieves a lower TCO via flat energy conversion efficiency over a wide load range, including improved efficiency of 5 percent to 15 percent across the full load range. The footprint savings are also impressive -- the 19-inch enclosure maximizes data center space for revenue-generating business requirements.

Sentilla's Energy Manager software platform and appliances were built to analyze data center and industrial energy profiles. With this insight, industries can minimize their global energy footprint, optimize their production processes and take positive action before problems become disasters.
How It Works: To help companies slash IT operating expenses and power costs, Sentilla Energy Manager analyzes energy use and waste at the equipment level to create actionable profiles of an organization's energy footprint. The resulting intelligence enables companies to conserve unused or wasted energy, resulting in diminished carbon emissions and dramatically lowered operating costs.

Cicso's EnergyWise program includes everything from comprehensive support to companies for reducing energy costs and greenhouse gas emissions, to the EnergyWise Business Value Calculator for estimating potential savings (pictured here).
How It Works: Cisco EnergyWise helps companies monitor the power of all Cisco network-connected devices, from Power over Ethernet (PoE) devices to IP-enabled building controllers; report aggregated power consumption to provide a clearer understanding of an organization's power-consumption habits; optimize overall power usage based on user-created policies across the entire corporate infrastructure; provide reports of current power conditions and suggest potential changes; and regulate companywide energy consumption using a scalable domain approach, which brings IT and facility networks together.
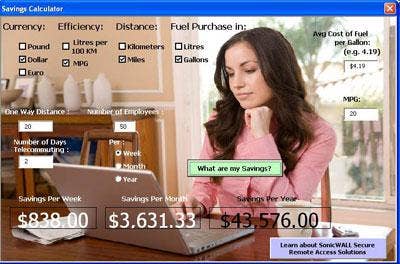
Here's another Green IT Calculator, this one courtesy of SonicWall. Designed as a useful tool for both employees and employers, the calculator helps companies calculate the cost and environmental savings of working green via telecommuting.
How It Works: Using the SonicWall Green IT Calculator, companies can determine how much money they can save their employees and contribute to saving the environment by implementing a telecommuting strategy. The calculator quantifies environmental savings over weeks, months and years, as well as the company's overall footprint on cost savings associated with hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and gas.

Data Domain's Global Compression technology greatly reduces the amount of disk space required to store data -- with typical data reduction rates of 20x to 30x, disk requirements are reduced by more than 95 percent thanks to the company's product.
How It Works: As an "inline" data deduplication technology, only unique new segments of data are ever stored to disk, significantly reducing the space, power and cooling needed for enterprise storage. In addition, as a global deduplication technology, WAN-based replication of data to -- or from -- other sites further reduces disk space and bandwidth requirements, as only new data is ever transferred across the network for remote storage.
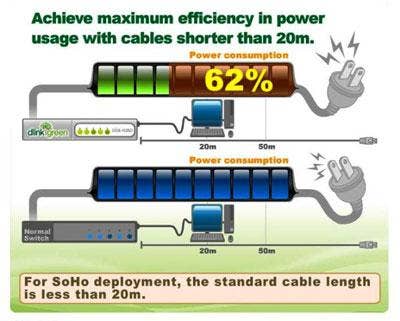
D-Link has initiated one of the computer networking industry's first Green Ethernet initiatives with a new series of environmentally friendly wired Ethernet switches for small businesses and home offices. The company is also in partnership with Energy Star, a joint program of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and the U.S. Department of Energy to promote energy conservation and management best practices.
How It Works: D-Link's high-performance switches can realize up to 80 percent savings in power usage by automatically adjusting power usage. The company also uses recycled materials in much of its packaging and is working to increase the percentage. D-Link products also comply with worldwide energy management standards, including the RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) and WEEE (Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment) directives.

Dot Hill's innovative EcoStor technology eliminates the use of cache backup batteries through the combination of super capacitor and flash memory technology. This feature is standard in the company's 2000 Series and 5000 Series storage arrays, such as the new Dot Hill 2722 SAS array (pictured).
How It Works: EcoStor removes the annual service costs and downtime associated with cache battery replacement, saves the environment from battery disposal, and provides a permanent backup of unwritten cache data in the event of a power outage, unlike traditional battery-based designs, which typically hold data for up to 72 hours, assuming a fully charged battery.
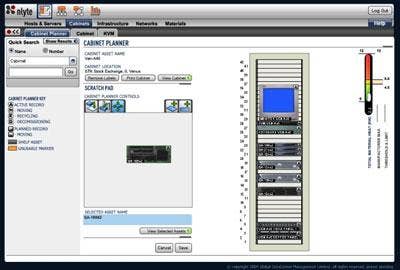
Global DataCenter Management's Nlyte software suite provides data center managers with a comprehensive view of their managed assets and provides automated solutions for typical management tasks, and the enforcement of standard processes and procedures. What's more, Nlyte lets users model changes in the data center before implementation to determine their impact on power, cooling and space allocation, as seen in this snapshot of the software's modeling console.
How It Works: Implementing a greener operation through Nlyte involves Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) Modeling, which virtually measures the effect of changes in the data center and the impact to PUE before physically making the changes. The result is intelligently managed power consumption that companies can leverage to both shrink their carbon footprint and optimize their critical data center infrastructure to drive down costs.

Lenovo's industry leadership in using post-consumer recycled plastics in the construction of many of its products is showcased in the ThinkStation D20 workstation (pictured here). The ThinkStation S20 workstation also contains the same amount of recycled content as its D20 cousin.
How It Works: Lenovo's ThinkStations are built from the equivalent of 19 plastic water bottles of post-consumer material per system. The company is credited with using a higher percentage of such recycled material in its products than its competitors, according to the widely recognized Electronic Product Environmental Assessment Tool (EPEAT) criteria. In 2008, Lenovo used more than 2.2 million pounds of post-consumer content to build its products, according to the company.

Isilon's IQ 36000X is a scale-out NAS platform that features leading usable capacity and utilization rates, meaning enterprise businesses can buy less physical storage while at the same time achieve more usable capacity with greater utilization than traditional SAN and NAS.
How It Works: Using Isilon's OneFS operating system software to create a single, highly scalable file system, the 36000X delivers utilization rates of more than 80 percent. When combined with Ocarina's ECOsystem compression and dedupe software, utilization increases to 90 percent, while reducing data at a 10-to-1 ratio, dramatically increasing system efficiency. In addition, with impressive disk density, the 36000X combines 36 1 TB drives in a 4U node to dramatically reduce the data center footprint of these scalable systems.

Western Digital's "green" hard drives include the consumer-oriented WD Caviar Green and the newly released RE4-GP, (pictured left), which is aimed at the enterprise market. Both hard drives have a whopping 2 TB of disk space and the RE4-GP in particular makes it possible for energy-conscious enterprise customers to build servers and storage subsystems with higher capacities, consistent performance and assured reliability, all while promoting energy conservation.
How It Works: WD's GreenPower technology platform reduces average drive power consumption by up to 50 percent over other products currently available on the market. The key WD technologies at play are IntelliPower, a fine-tuned balance of spin speed, transfer rate and caching algorithms; IntelliPark, which automatically unloads recording heads during idle to reduce aerodynamic drag, and disengages read/write channel electronics; and IntelliSeek, which calculates optimum seek speeds to lower power consumption, noise and vibration.
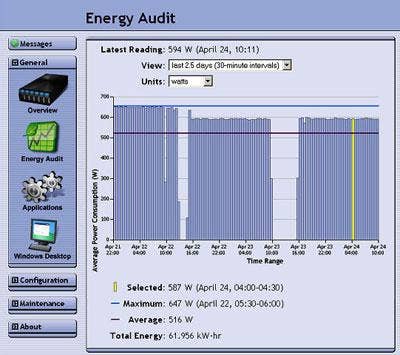
The methods for calculating the power use of a tape library typically have been performed manually using specifications (usually based on 100 percent or worst-case load) and a calculator. Spectra Logic decided that this approach wasn't enough -- so now, power monitoring is part of the company's BlueScale interface through EnergyAudit.
How It Works: This patented technology allows for real-time monitoring, which gives the user a chance to check actual power use and balance the energy load in data centers.The power-monitoring feature taps directly into the power supply to check out how much power is in use, and can report the data using measurements of watts-per-cubic-foot and watts-per-square-foot of data center space, as well as watts-per-terabyte of media capacity in a tape library.
The Compellent Storage Center storage area network (SAN) offers a number of advanced data management applications, which are designed to reduce power and cooling requirements, decrease the size of the data center footprint and increase energy-efficiency. The Compellent SAN employs automated tiered storage to dynamically migrate blocks of data between tiers of storage based on frequency of access.
How It Works: Older blocks of data automatically move from high-performance and energy-hungry Fibre Channel drives to more energy-efficient SATA drives, which leads to significant power savings. Compellent's thin provisioning increases storage utilization by eliminating allocated but unused capacity, and enables users of the company's Enterprise Manager software, (shown here), to report how they've allocated any size virtual volume up front, yet only consumed actual physical capacity when data is written by the application.
One way to cut power consumption is to cut power to devices that are not in use. That's the principle behind Extreme Networks' Universal Port Technology line of network ports.
How It Works: Extreme Networks' Universal Port technology helps make networks more energy-efficient and intelligent by allowing network managers to power down non-essential PoE (Power over Ethernet)-powered end-points, such as IP phones, during set hours. In a school environment, for instance, Universal Port can power down phones on weekends or holidays to cut energy costs.Universal Port is also used for simplifying edge device configuration and for automating the activation of user profiles. This feature is embedded in all Extreme Networks switches running the ExtremeXOS operating system.
Data deduplication, or dedupe, is a fundamental component of NetApp's Data ONTAP operating system, which is at the heart of the company's networked storage appliance family. Dedupe is offered by the company for use broadly across multiple applications and storage tiers, including primary data, backup data and archival data. The use of NetApp deduplication in conjunction with strong data management policies reduces the need for disk drive expansion, thus lowering power and cooling requirements.
How It Works: Deduplication removes duplicate information as data is stored, backed up or archived. It can be done at the file level, where duplicate files are replaced with a marker pointing to one copy of the file, and/or at the sub-file or byte level, where duplicate bytes of data are removed and replaced by pointers, resulting in a significant decrease in storage-capacity requirements.

One way to make a system more "green" is to cut down on the waste generated in the manufacturing process. Startup Axcient does that in addition to cutting power consumption in its new small business backup appliance combined with an off-site storage vault.
How It Works: Axcient has deployed only half-height DIMM modules to reduce the total amount of waste by 40 percent and power consumption by 33 percent compared to traditional DIMMs. The new, low-profile modules function the same way as the full-height modules, but allow the appliances to benefit from smaller systems and lower heat diffusivity. These modules follow the JEDEC standard for cutting the power consumption of printed circuit boards (PCBs). As a result, during normal operation, power consumption of the appliance is only about 55 Watts, compared to about 30 Watts when it is in idle mode.

Hitachi Data Systems subscribes to the Hitachi Environmental Vision for 2025, which targets the reduction of annual CO2 emissions by 100 million tons for all Hitachi products by 2025. To achieve this, Hitachi has implemented eco certifications -- Certified Super Eco Products and Certified Eco Products -- for all its products. By 2010, Hitachi aims to have 30 percent of all products Super Eco certified, and 100 percent of products Eco Certified. The company's Hitachi USP V/VM and AMS 2000 storage products are already Super Eco-certified. Hitachi also plans to open the world's largest green data center later this summer in Yokohama, Japan. The Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) of this Data Center aims to be the lowest in the industry, at a 1.6 rating (a PUE value approaching 1.0 indicates 100 percent efficiency).
How It Works: The Hitachi Universal Storage Platform V (USP V) allows the virtualization of Hitachi and third-party storage to help end users increase utilization rates and reduce storage CAPEX and OPEX to increase their return on invested assets. That technology can increase storage utilization by up to 40 percent and reclaim stranded capacity by up to 50 percent.

In January 2008, EMC released the first enterprise storage system with Flash-based solid state drives (SSDs). By the end of 2008, Flash drives were available in the company's Symmetrix and CLARiiON systems. Earlier this year, EMC unveiled the availability of new, larger-capacity, second-generation enterprise flash drives for its market-leading EMC Symmetrix.
How It Works: Flash drives are an order of magnitude faster than the fastest hard disk drives and require dramatically less power to run. Because there are no mechanical components, flash drives use 38 percent less energy per terabyte of data stored than traditional mechanical disk drives. In addition, it can take up to 30 mechanical disk drives to deliver the same speed of performance as a single flash drive, which translates into a dramatic 98 percent reduction in power consumption in a transaction-per-second comparison.