The 10 Coolest AI Chips Of 2021 (So Far)
Nvidia may hold the crown in the AI chip market right now, but there are many companies hoping to outgun the GPU juggernaut with new, unique processor architectures. CRN takes a look at the coolest AI chips this year so far, from vendors both small and large.

The Race To Make Faster, More Efficient AI Chips Continues
Deep learning models keep getting bigger, and AI-powered devices keep getting smaller, which means there is plenty of room for innovation in the chips that make such applications possible.
The race to make faster, more efficient AI chips has many contestants, and they range from the world’s largest providers of cloud computing to small startups making chips for edge devices. Nvidia may hold the crown in the AI chip market right now, but many of these companies are hoping to outgun the GPU juggernaut with new, unique processor architectures.
[Related: The 10 Hottest Semiconductor Startups Of 2021 (So Far)]
What follows are the 10 coolest AI chips of 2021 so far.

Ambarella CV52S
Ambarella recently announced an expansion of its AI vision system-on-chip portfolio with the new CV52S and CV5S chip families for 4K security cameras. The new SoCs are built using the company’s CVflow architecture and an advanced 5-nanometer manufacturing process, and they can support multiple streams of 4K encoding and advanced AI processing. This is all done in a single low-power design, which the company says “provides industry-leading edge AI SoC performance per watt.” The company is positioning the CV52S for single-sensor security cameras with advanced AI performance that can provide better accuracy in identifying objects and individuals. The CV5S, on the other hand, is meant to security cameras with multiple sensors that provide 360-degree coverage.

Atlazo AZ-N1
Atlazo is looking to power AI and machine learning workloads in tiny smart devices with its first-generation system-on-chip, the AZ-N1. Announced in January, the startup says the AZ-N1 includes its highly power efficient AI and machine learning processor, the Axon I, which is targeted for audio, vice, health monitoring and sensor use cases. Atlazo says one Axon I processor can perform more than 130 inferences, and there are a variety of products in development that will use the AZ-N1, including smart earbuds, hearing aids and health monitoring devices. Aside from its processing horsepower, the AZ-N1 also includes a low-power CODEC that can support up to four microphones, a battery charge, DC/DC regulators and Bluetooth connectivity.

AWS Trainium
Amazon Web Services says it will deliver the “most cost-effective training in the cloud” with Trainium, its new custom-designed chip that will be available in instances sometime this year. Andy Jassy, then-CEO of AWS, announced the chip at AWS re:Invent 2020 in December and said it will even be more cost effective than Intel’s Habana Gaudi chips, which he touted as providing up to 40 percent better price-performance than Nvidia GPUs running in AWS cloud instances. The chip shares the same AWS Neuron software development kit as AWS Inferentia, AWS’ first custom-designed chip for machine learning. Trainium is optimized for deep learning training workloads that include image classification, semantic search, translation, voice recognition, natural language processing and recommendation engines.

Cerebras Wafer Scale Engine 2
Cerebras Systems says its Wafer Scale Engine 2 chip is the “largest AI processor ever made,” consisting of 2.6 trillion transistors, 850,000 cores and 40GB of on-chip memory. The startup says those specifications give the WSE-2 chip a massive advantage over GPU competitors, with 123 times more cores and 1,000 times more on-chip memory. Revealed earlier this year, the WSE-2 chip powers Cerebras’ purpose-built CS-2 system, which “delivers more compute performance at less space and less power than any other system,” according to the startup. More specifically, Cerebras says the CS-2 can deliver hundreds of thousands of times more performance than alternatives depending on the workload, and a single system can replace clusters consisting of hundreds or thousands of GPUs.

Google TPU v4
Google’s TPU v4 is the latest generation of the company’s Tensor Processing Units that are used to power internal machine learning workloads and some Google Cloud instances. Google CEO Sundar Pichai announced the new TPUs at the Google I/O event in May, saying that the TPU v4 provides more than double the performance of the previous generation. When 4,096 of them are combined into a TPU v4 Pod, the system can deliver 1.1 exaflops of peak performance, according to Google, which is equivalent to more than a quintillion mathematical equations per second. The company recently announced that the TPU v4 was able to set new performance records in four MLPerf benchmarks, which showed that the chip was faster than Nvidia’s A100 GPU.

3rd-Gen Intel Xeon Scalable (Ice Lake)
Intel’s new third-generation Xeon Scalable CPUs are not dedicated AI accelerators like the rest of the computer chips in this list, but the chipmaker says the processors, code-named Ice Lake, are the only data center CPUs with built-in AI capabilities. This is made possible by Ice Lake’s Intel DL Boost feature, which consists of Vector Neural Network Instructions for accelerating inference workloads. Ice Lake also comes with Intel Advanced Vector Extensions 512, or Intel AVX-512, to boost machine learning performance. The chipmaker has touted that Ice Lake can provide 30 percent better performance than Nvidia’s A100 GPU “across a broad mix of 20 popular AI and machine learning workloads.”

Mythic M1076 Analog Matrix Processor
Mythic is promising best-in-class performance, scalability and efficiency with its recently revealed M1076 Analog Matrix Processor, also known as Mythic AMP. The Redwood City, Calif.-based startup says the M1076 AMP can perform up to 25 trillion operations per seconds of AI compute performance in a small 3-watt power envelope, requiring 10 times less power than GPU or system-on-chip alternatives. The new processors support use cases ranging from video analytics to augmented reality, and they come in a variety of form factors, from an ultra-compact PCIe M.2 card to a PCIe card that contains 16 AMPs.

Nvidia A100
Nvidia’s A100 is the chipmaker’s flagship data center GPU for inference and training, and while it was first introduced last year, it continues to dominate multiple benchmarks for AI performance. The chipmaker recently announced that the A100 broke 16 AI performance records in the latest MLPerf benchmarks, which Nvidia says makes the GPU the fastest for training performance among commercially available products. The A100 is now available in 40GB and 80GB memory models across PCIe and AXM form factors. The company says the A100 can outperform its previous-generation V100 and T4 GPUs several times over. The A100’s top features include multi-instance GPU, structural sparsity and support for the new TF32 format.
Syntiant NDP120
Syntiant wants to bring low-power edge devices to the next level with its new NDP120 Neural Decision Processor. Revealed in January, the NDP120 uses neural processing to enable battery-powered devices to run multiple applications without having a major impact on battery. The NDP120 is the first chip to use the startup’s Syntiant Core 2 tensor processor platform, which supports more than 7 million parameters and “can process multiple concurrent heterogenous networks,” according to the startup. In addition to the Syntiant Core 2 neural processor, the NDP120 includes an Arm Cortex M0 microcontroller, onboard firmware decryption and authentication and support for up to seven audio streams, among other things. Targeted use cases include mobile phones, earbuds, wearables, smart speakers, laptops, smart home applications and security devices.
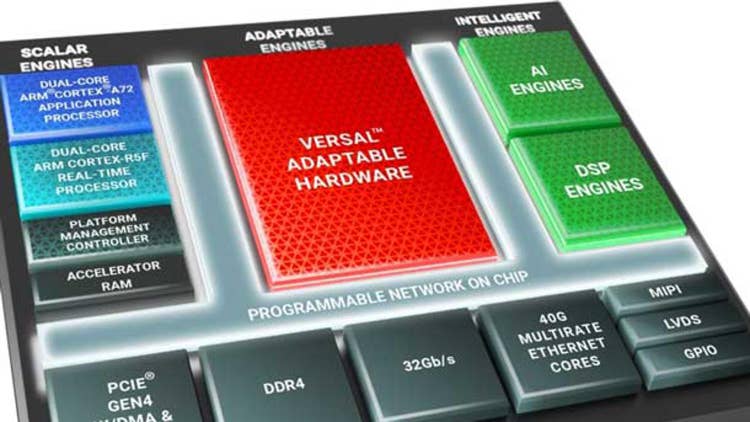
Xilinx Versal AI Edge
Xilinx says that its upcoming Versal AI Edge series of chips will provide four times greater AI performance per watt versus Nvidia’s top GPU for edge computing, the Jetson AGX Xavier. The company recently announced the new series of chips, which is called the “world’s most scalable and adaptable portfolio for next-generation distributed intelligent systems.” Xilinx says it will deliver a major performance-per-watt advantage over GPUs thanks in part to a new AI Engine architecture that provides four times greater machine learning compute than the previous generation. Also contributing to Versal AI Edge’s competitiveness is a new accelerator RAM module with enhanced memory hierarchy. The new chips will be fully software-programmable and target applications ranging from automated driving and collaborative robotics to predictive factory and healthcare systems.