10 New AWS Tools To Know About In 2021
CRN provides a look at new Amazon Web Services products and services slated to launch in 2021 and a few others to watch this year.

As Amazon Web Services starts the new year, still comfortably ensconced as the world’s largest cloud provider, its customers await some of the new products and services that it preannounced at December’s virtual AWS re:Invent 2020 conference as coming this year.
Those forthcoming solutions include the AWS Trainium custom machine learning (ML) chip, new on-premises deployment options for Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon ECS), and the open source project for the new Babelfish for Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL , which allows Microsoft SQL Server customers to move to less expensive PostgreSQL databases.
AWS also promised new smaller form factors of its AWS Outposts hybrid cloud offering and a dozen new U.S. metro locations for AWS Local Zones, extensions of AWS cloud regions where customers can run their latency-sensitive applications using AWS services.
Here’s a look at those new products and services scheduled to launch in 2021 and others to watch as the year unfolds.
See the newest entry: The 10 Coolest New AWS Tools Of 2022 (So Far)

Smaller AWS Outposts
At re:Invent 2020, AWS showcased two new smaller formats of AWS Outposts, its fully managed hybrid cloud offering that extends AWS infrastructure, services, APIs and tools to virtually any customer data center, co-location space or on-premises facility.
With Outposts, customers get compute-and-storage racks built with AWS-designed hardware that are installed and maintained by AWS. The initial rack that AWS launched with about a year ago is an industry-standard 42U measuring 80 inches tall, 24 inches wide and 48 inches deep.
The new smaller Outposts form factors – 1U and 2U rack-mountable servers – have the same functionalities as the initial rack, but they allow customers to run AWS infrastructure in locations with less space. The 1U size is 1 ¾ inches tall -- about the size of a pizza box, according to AWS CEO Andy Jassy -- and 40th the size of the Outposts launch rack. The 2U size is about 3 1/2 inches tall or almost two pizza boxes stacked.
The smaller AWS Outposts form factors will be available this year.
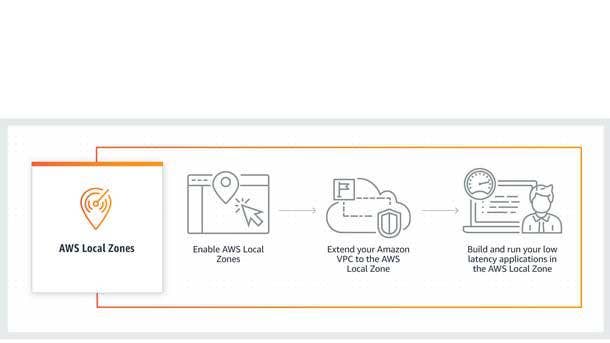
More Local Zones
At re:Invent 2020, AWS also gave notice of three new AWS Local Zones in preview in Boston, Houston and Miami, and its plans to launch additional Local Zones in 12 other U.S. cities this year.
A newer type of AWS infrastructure, AWS Local Zones allow customers to use certain core AWS services -- including compute, storage and database services -- to run applications that require single-digit millisecond latency in closer geographic proximity to their end-users. Local Zones are designed for areas where there are no AWS cloud regions and for customers that don’t want to maintain their own data centers or use co-location facilities. The Local Zones are connected to an AWS parent region by a redundant, high-bandwidth, private AWS network, and they provide customers a secure connection between their local workloads and their workloads running in the closest AWS Region.
AWS Local Zones use cases include real-time gaming, live video streaming, ML inference, and media and entertainment content creation, according to AWS.
The cloud provider announced its first AWS Local Zone -- in Los Angeles for end-users in the southern California area -- at re:Invent 2019.
The other Local Zones slated to launch this year will be in Atlanta, Chicago, Dallas, Denver, Kansas City, Las Vegas, Minneapolis, New York, Philadelphia, Phoenix, Portland and Seattle.
Amazon EC2 Mac Instances
Apple’s more than 28 million developers now can use new Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) Mac instances to natively run on-demand macOS workloads in the AWS cloud for the first time to develop, build, test and sign Apple applications for the iPhone, iPad, Mac, Apple Watch, Apple TV and Safari.
Developers can provision and access macOS environments within minutes and dynamically scale capacity as needed while benefiting from AWS’ pay-as-you-go pricing, according to the cloud provider, which revealed the new offering in November. The EC2 Mac instances can be used with AWS services and features including Amazon Virtual Private Cloud for network security, Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) for expandable storage, Amazon Elastic Load Balancer for distributing build queues and Amazon Machine Images for OS image orchestration, according to AWS.
The EC2 Mac instances are powered by the AWS Nitro System and are built on Apple Mac mini-computers with Intel’s eighth-generation, 3.2 GHz (4.6GHz turbo) Core i7 processors, six physical/12 logical cores and 32 GiB of memory. Customers have a choice of both macOS Mojave (version 10.14) and macOS Catalina (10.15) operating systems, with support for macOS Big Sur (11.0) coming soon.
The EC2 Mac instances currently are available in AWS’ U.S. East (northern Virginia), U.S. East (Ohio), U.S. West (Oregon), Europe (Ireland) and Asia-Pacific (Singapore) cloud regions.

New AWS Graviton2-powered C6g Instances
AWS delivered new Amazon EC2 instances powered by its AWS-designed Graviton2 processors. Graviton2 is AWS’ next generation Arm-based chip that gives customers up to 40 percent better price performance than the most recent generations of x86 processors from other providers, according to AWS.
Unveiled at AWS re:Invent 2020, new C6gn instances are available in eight sizes. They provide up to 64 vCPUs,100 gigabits per second of network bandwidth and 38 gigabits per second of Amazon EBS bandwidth for compute- and network-intensive workloads. C6gn instances provide the best packet processing performance on EC2, according to AWS, allowing customers to migrate to C6gn and consolidate their workloads onto fewer instances or smaller instance sizes and reduce infrastructure costs.
Last June, AWS also heralded the general availability of new Amazon EC2 C6g and R6g instances after launching its general-purpose EC2 M6g instances last May. All are powered by Graviton2 processors. AWS designed the C6g instances for compute-intensive workloads, including high-performance computing, batch processing, video encoding, gaming, scientific modeling, distributed analytics, ad-serving and CPU-based machine learning inference. The R6g instances are for workloads that process large data sets in memory, including open-source databases such as MySQL, MariaDB and PostgreSQL; in-memory caches such as Redis, Memcached and KeyDB; and real-time, big data analytics.
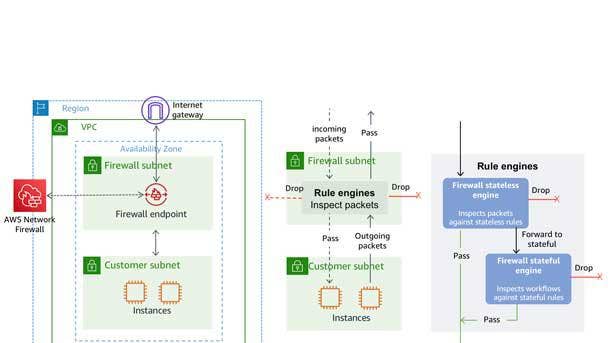
AWS Network Firewall
AWS Network Firewall is a new stateful, high-availability firewall service for virtual private clouds (VPCs) created in Amazon VPC.
The managed security service, introduced in November, allows users to filter traffic at the perimeter of their VPCs, including traffic coming and going from an internet gateway, network address translation gateway or over a virtual private network or AWS Direct Connect. It uses Suricata, the open-source intrusion prevention system for stateful inspection, and supports Suricata-compatible rules.
AWS Network Firewall is available in AWS’ U.S. East (northern Virginia), U.S. West (Oregon) and Europe (Ireland) cloud regions. Customers can enable AWS Network Firewall with a few clicks in the AWS Console, and it automatically scales with network traffic without having to set up or maintain the underlying infrastructure.
But as CRN’s Michael Novinson reported in November, solution providers are doubtful that AWS Network Firewall will appeal to large enterprises with robust security needs across multiple public cloud platforms, because it lacks multi-vendor protection and comes with “bare minimum” features.
“It looks like a basic firewall with intrusion prevention,” one solution provider, who didn’t want to be identified, told Novinson. “It’s better than the bare minimum they were providing before, but anyone serious, such as large enterprises, will still go for a top-tier solution such as Palo Alto, Check Point or Fortinet.”
AWS says AWS Network Firewall’s flexible rules engine gives customers “granular control to define their own custom rules or integrate with their existing security ecosystem by importing rules from leading AWS security partners like AlertLogic, CrowdStrike, Fortinet, and Trend Micro.”

Aqua For Amazon Redshift
AQUA (Advanced Query Accelerator) for Amazon Redshift provides a new distributed, hardware-accelerated cache that brings compute to the storage layer for Amazon Redshift, AWS’ cloud data warehouse.
AQUA is a high-speed cache on top of Redshift Managed Storage. It does a significant share of data processing in-place on the cache, and AWS-designed analytics processors and a scale-out architecture accelerate data processing beyond what traditional CPUs can do, according to AWS. The processors accelerate data compression, encryption and data processing on queries that scan, filter and aggregate large data sets, with AQUA delivering up to 10x faster query performance than other cloud data warehouses, according to AWS.
AQUA is available with the Amazon Redshift RA3.16XL and RA3.4XL nodes at no additional cost and doesn’t require code changes. In preview in AWS’ U.S. East (Ohio), U.S. East (northern Virginia) and U.S. West (Oregon) cloud regions, AQUA is slated to become generally available this month.

AWS Trainium
AWS Trainium is a high-performance ML training chip custom-designed by AWS to deliver the most cost-effective training in the cloud, Jassy said at re:Invent 2020. It shares the same AWS Neuron software development kit as AWS Inferentia, AWS’ first custom-designed, ML inference chip launched at re:Invent 2019.
“Trainium will be even more cost-effective than the Habana chip,” Jassy said. “It’ll support all the major frameworks -- TensorFlow and PyTorch and MX Net.”
AWS Trainium provides the highest performance with the most teraflops of compute power for ML in the cloud, according to AWS, and it enables a broader set of ML applications. The chip is optimized specifically for deep learning training workloads for applications including image classification, semantic search, translation, voice recognition, natural language processing and recommendation engines.
AWS Trainium will be available in the second half of this year via Amazon EC2 instances, AWS Deep Learning AMIs and managed services including Amazon SageMaker, Amazon ECS, Amazon EKS and AWS Batch, according to AWS. Because its Neuron SDK is integrated with ML frameworks including TensorFlow, PyTorch and MXNet, developers can easily migrate from GPU-based instances to AWS Trainium with minimal code changes, AWS said.
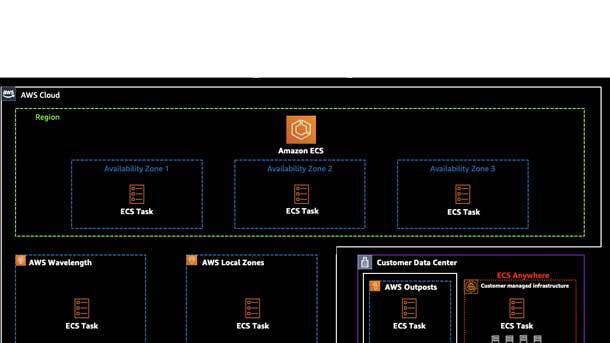
Amazon ECS Anywhere And Amazon EKS Anywhere
Amazon ECS Anywhere and Amazon EKS Anywhere are designed to make it easier for customers to provision, deploy and manage container applications on premises in customers’ own data centers. Both are expected to be available in the first half of this year.
While AWS had three container offerings – AWS Fargate in addition to Amazon ECS and Amazon EKS -- customers still have a lot of containers that need to run on premises while they transition to the cloud, and they wanted the same management and deployment mechanisms on premises that they have in AWS, according to Jassy.
Amazon ECS Anywhere allows customers to run Amazon ECS -- a cloud-based, fully managed container orchestration service – to orchestrate containers in customer-managed infrastructure and traditional AWS managed infrastructure. Customers get the same AWS-style APIs and cluster configuration management pieces on premises that are available in the cloud. It precludes them from having to run or maintain their own container orchestrators on-premises.
Amazon EKS Anywhere is a new deployment method for Amazon EKS, a managed service that allows customers to run Kubernetes on AWS without dealing with their own Kubernetes control plane or nodes.
Amazon EKS Anywhere allows customers to create and operate Kubernetes clusters on-premises, including on their own virtual machines and bare metal servers. It gives them consistent Kubernetes management tooling that’s optimized to simplify cluster installation with default configurations for OS, container registry, logging, monitoring, networking and storage, according to AWS. It uses Amazon EKS Distro, the same open-source Kubernetes distribution deployed by Amazon EKS for customers to manually create Kubernetes clusters.
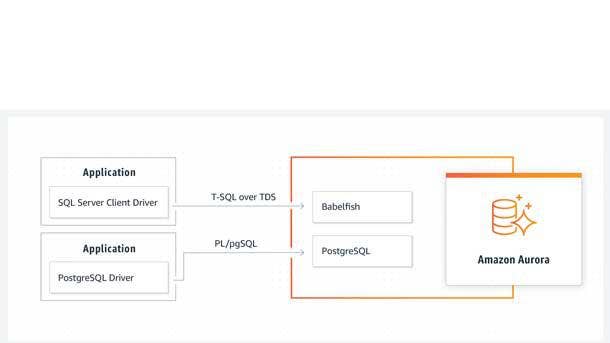
Babelfish For Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL
Babelfish for Aurora PostgreSQL allows Microsoft SQL Server customers to move to less expensive PostgreSQL databases. It lets them run Microsoft SQL Server applications directly on Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL with little to no code changes.
Babelfish provides a new translation layer for Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL that enables Aurora to understand commands from applications written for Microsoft SQL Server. It enables Aurora PostgreSQL to understand T-SQL, Microsoft SQL Server’s proprietary SQL dialect, and supports the same communications protocol, precluding customers from having to rewrite all their applications’ database requests.
Babelfish for Aurora PostgreSQL is now in limited private preview, with a broader preview expected later this year.
Customers had told AWS that they use the AWS Database Migration Service to move their database data, and they use AWS’ Schema Conversion Tool to convert the schema, but there was a third area that was harder than they hoped -- figuring out what to do with the application code that is tied to that proprietary database, according to Jassy.
Babelfish is a built-in feature of Amazon Aurora available at no additional cost and can be enabled on an Amazon Aurora cluster with a few clicks in the RDS management console. After migrating their data using AWS Data Migration Services, customers can update their application configuration to point to Amazon Aurora instead of SQL Server and start testing the application running on Amazon Aurora instead of SQL Server. Once customers have tested the application, they no longer need SQL Server and can “shed those expensive and constrained SQL Server licenses,” according to Jassy.
AWS plans to open source Babelfish for PostgreSQL under the permissive Apache 2.0 license and make it available on GitHub this year.
Amazon Aurora Serverless v2
AWS last month announced the next generation of Amazon Aurora Serverless, the on-demand, auto-scaling configuration for the Amazon Aurora relational database service, which is AWS’ fastest growing service in its history.
Aurora Serverless v2 scales to hundreds of thousands of transactions in a fraction of a second, according to AWS, delivering up to 90 percent cost savings when compared to provisioning for peak capacity.
“Aurora Serverless v2 totally changes the game for you with serverless as it relates to Aurora,” Jassy said at re:Invent 2020. “You can scale up as big as you need to instantaneously. It only scales you up in the precise increments that you need. It adds in a lot of the Aurora capabilities people wanted: multi AZ and Global Database and read replicas and backtrack and Parallel Query, and it really makes Aurora Serverless v2 ideal for virtually every Aurora workload.”
Amazon Aurora Serverless v2 is available in preview for the MySQL 5.7-compatible edition of Amazon Aurora and will be available for PostgreSQL in the first half of 2021.